- Institute
- Research topics
- Organization
- Platforms
- Services
- Europe/International
- Science outreach
- Agenda
- Directory
- Access
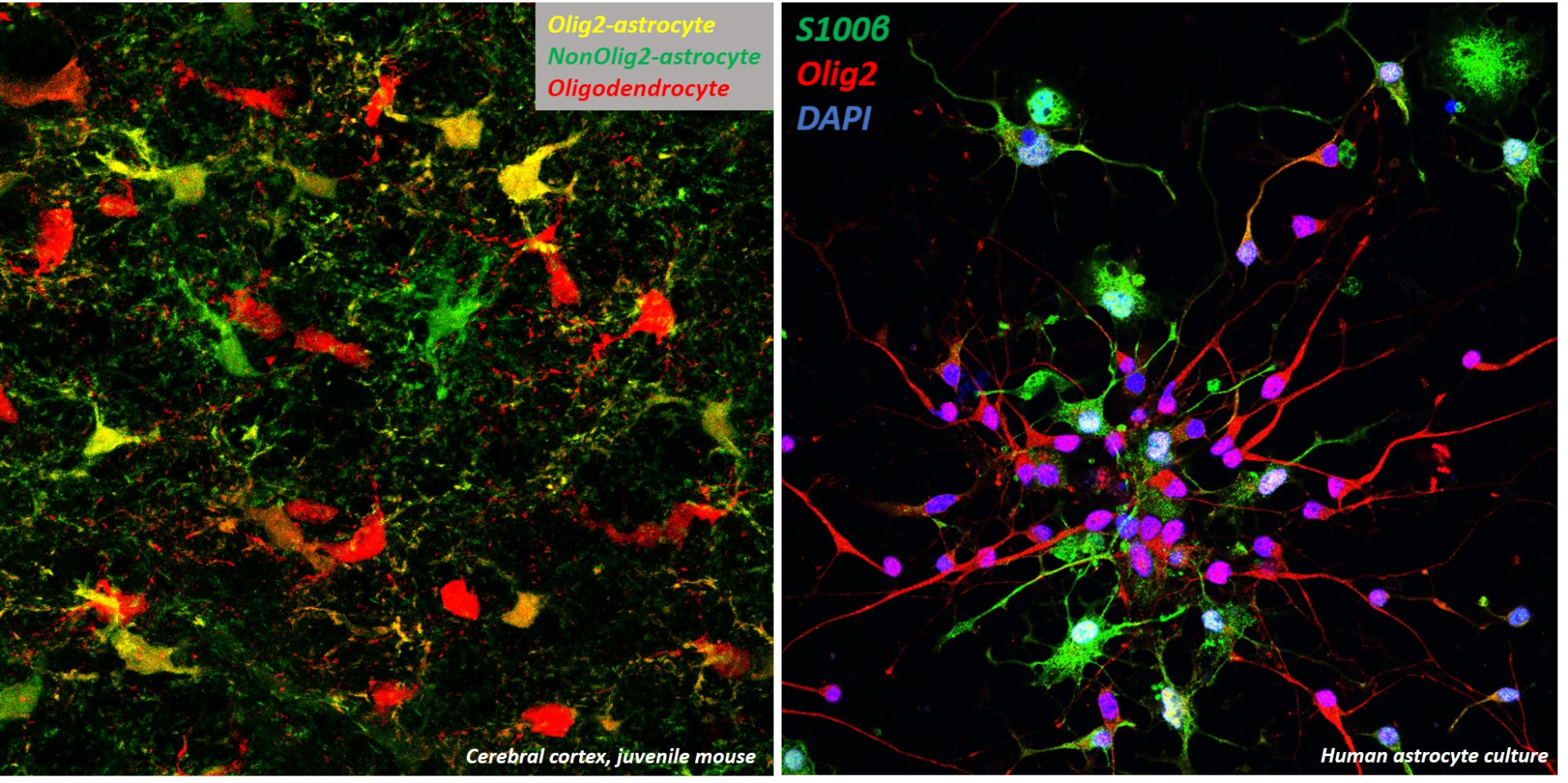
Astrocytes participate in a wide variety of complex and essential functions in the central nervous system (CNS), including synaptic development and plasticity, trophic regulation and blood-brain barrier formation. Work over the last decades has allowed significant advance in unravelling the complexity of macroglial cell functions, highlighting the existence of a far greater level of heterogeneity among macroglial cells than previously considered. The question of macroglial cell heterogeneity, especially for astrocytes, remains open, as the contribution of this diversity to normal CNS function and in disease is still unclear. Recent work led us to evidence an unidentified sub-population of astrocytes (Olig2-AS) in mouse that can be distinguished from other astrocyte populations by the expression of Olig2, a transcription factor currently recognized as a hallmark of oligodendrocytes (Ohayon et al., 2019; Ohayon et al., 2021). Our goal is to approach the question of the functional specificity of this Olig2-AS during development in physiological and pathological brain.
Experimental approaches we use in the lab includes gene profiling, cellular/behavioural analysis in transgenic mouse models and in vitro models of astrocytes derived from hiPSCs.

